Problem Statement
Given an array of sorted numbers, remove all duplicates from it. You should not use any extra space; after removing the duplicates in place return the length of the subarray that has no duplicate in it.
Example 1:
Input: [2, 3, 3, 3, 6, 9, 9]
Output: 4
Explanation: The first four elements after removing the duplicates will be [2, 3, 6, 9].
Example 2:
Input: [2, 2, 2, 11]
Output: 2
Explanation: The first two elements after removing the duplicates will be [2, 11]
So how do we solve this ? Let's put our thinking caps on! ......
After thinking for a while, you might find a solution where you use a two-pointer and just count the repeated elements. Which gives you the answer.
def remove_duplicates(arr):
duplicates = 0
for pointer_start in range(1, len(arr)):
pointer_end = pointer_start - 1
if arr[pointer_start] == arr[pointer_end]:
duplicates += 1
return len(arr) - duplicates
print(remove_duplicates([2, 3, 3, 3, 6, 9, 9]))
print(remove_duplicates([2, 2, 2, 11]))
Output:
4
2
But We should not forget the given condition
You should remove all duplicates from the array ! Now one might ask that the arrays are immutable. I understand your confusion, Array size is immutable not the array itself. So we can manipulate the data once created not the size !.
So how should one solve this ?
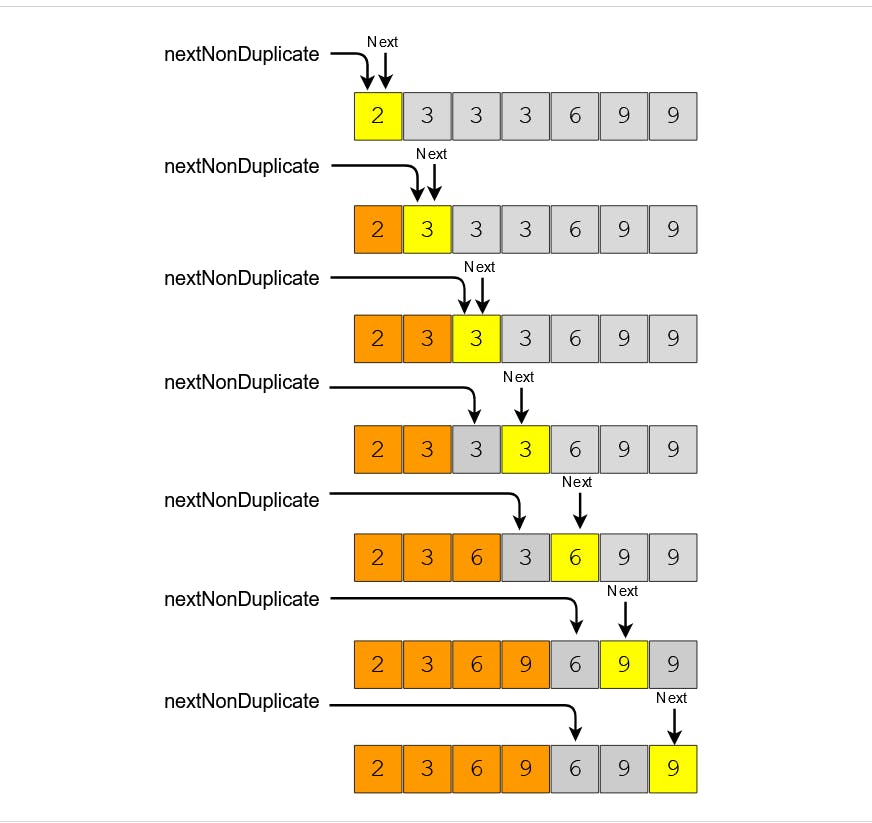
This is a very good explanation I found online. What are we doing is we are taking two pointers
- Next
- nextNonDuplicate
We traverse two pointers just as shown in the image.
def remove_duplicates(arr):
# index of the next non-duplicate element
next_non_duplicate = 1
i = 1
while(i < len(arr)):
if arr[next_non_duplicate - 1] != arr[i]:
arr[next_non_duplicate] = arr[i]
next_non_duplicate += 1
i += 1
return next_non_duplicate
